LaravelでCORSを有効にしたいときの方法を紹介します。
CORSを有効にするには?
原理的には、ヘッダーに以下の内容を追加することができれば、クロスオリジンでアクセスすることができるようになります。
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin:*
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods:GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers:Content-Type
すべてのアクセスに対し、以上のヘッダーを追加すれば、CORSが有効になります。
LaravelでCORSを有効にする方法
Laravelで実現するには2つの方法があります。
- ライブラリ「fruitcake/laravel-cors」をつかう
- ミドルウェアでヘッダーを追加する
どちらでも対応することができます。
ただ、自前で実装すると大変なところもあるため、1のほうがおすすめです。当記事では1のライブラリ「laravel-cors」を使用した方法を紹介します。
手順
fruitcake/laravel-corsをインストール
composerでfruitcake/laravel-corsをインストールします。
composer require fruitcake/laravel-corsグローバルミドルウェアに追加する
すべてのアクセスを処理するミドルウェアとして、fruitcake/laravel-corsを追加します。
グローバルミドルウェアは、app/Http/Kernelから登録できます。
<?php
namespace App\Http;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Kernel as HttpKernel;
class Kernel extends HttpKernel
{
/**
* The application's global HTTP middleware stack.
*
* These middleware are run during every request to your application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $middleware = [
\Fruitcake\Cors\HandleCors::class,//追加
\App\Http\Middleware\TrustProxies::class,
\App\Http\Middleware\CheckForMaintenanceMode::class,
\Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\ValidatePostSize::class,
\App\Http\Middleware\TrimStrings::class,
\Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Middleware\ConvertEmptyStringsToNull::class,
];
CORSの設定ファイルを作成する
CORSに関する設定を記述するファイルを作成します。
とはいえ、コマンドから自動的に生成できます。
php artisan vendor:publish --tag="cors"すべてのアクセスをCORS許可にするには、デフォルトのままでOKです。
<?php
return [
/*
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Laravel CORS Options
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| The allowed_methods and allowed_headers options are case-insensitive.
|
| You don't need to provide both allowed_origins and allowed_origins_patterns.
| If one of the strings passed matches, it is considered a valid origin.
|
| If ['*'] is provided to allowed_methods, allowed_origins or allowed_headers
| all methods / origins / headers are allowed.
|
*/
/*
* You can enable CORS for 1 or multiple paths.
* Example: ['api/*']
*/
'paths' => ['*'],
/*
* Matches the request method. `['*']` allows all methods.
*/
'allowed_methods' => ['*'],
/*
* Matches the request origin. `['*']` allows all origins. Wildcards can be used, eg `*.mydomain.com`
*/
'allowed_origins' => ['*'],
/*
* Patterns that can be used with `preg_match` to match the origin.
*/
'allowed_origins_patterns' => [],
/*
* Sets the Access-Control-Allow-Headers response header. `['*']` allows all headers.
*/
'allowed_headers' => ['*'],
/*
* Sets the Access-Control-Expose-Headers response header with these headers.
*/
'exposed_headers' => [],
/*
* Sets the Access-Control-Max-Age response header when > 0.
*/
'max_age' => 0,
/*
* Sets the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials header.
*/
'supports_credentials' => false,
];
完成!
これだけでCORSが許可されるようになります。
DevToolで確認してみると、たしかにCORSが許可されています。
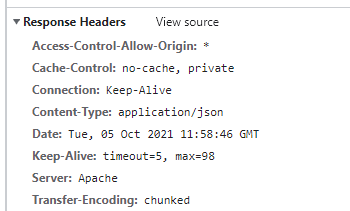
自前で実装しても大した手間ではないですが、特段の理由がない限りはfruitcake/laravel-corsを使用するのがよいでしょう。ドメインを指定したり、いろいろとできるようになっています。
注意すべきはデバッグ時です。
fruitcake/laravel-corsを導入しても、ddなどの一部の出力はクロスオリジンでアクセスすると、エラーとなります。
また、404などのレスポンスエラーの際も、クロスオリジンでアクセスした場合はCORSエラーとなってしまい、ブラウザで正しくレスポンスを受け取れない場合(例えば500エラーなのにブラウザではCORSエラー表示されてしまうなど)があります。
状況によって異なりますが、意図しないCORSエラーが起こったときは、一度プログラムが正しく動作しているかチェックするのがよいでしょう。




コメント